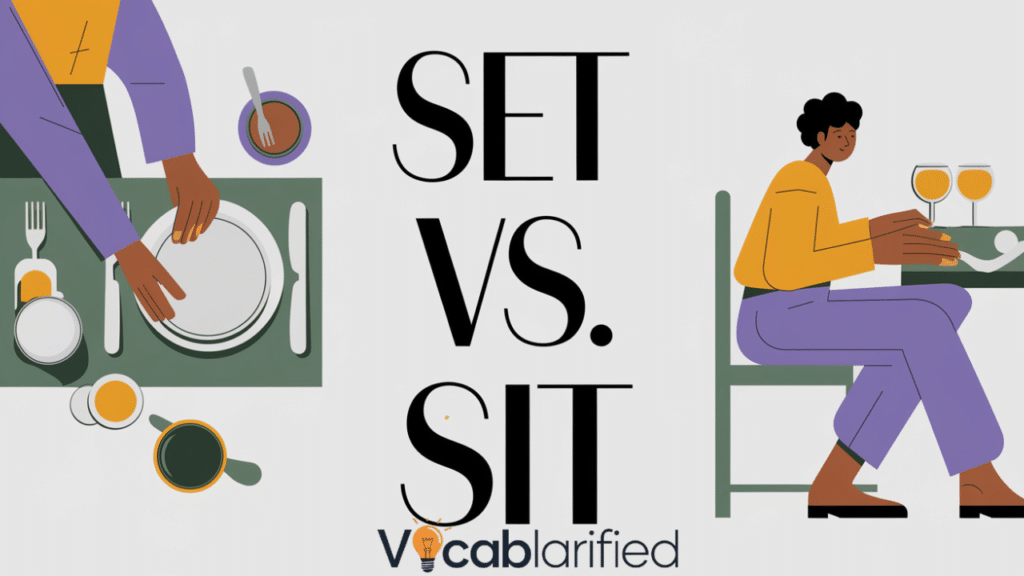
English grammar can be a labyrinth of complexities, with certain verbs causing particular confusion for language learners and native speakers alike.
The verbs set and sit represent a classic example of words that seem deceptively similar but carry distinct meanings and verb usage patterns.
The Fundamental Difference
Transitive verbs and intransitive verbs play a crucial role in understanding the nuanced application of set and sit. Set typically involves arranging or positioning something, while sit relates to the action of taking a seated position.
| Verb Type | Definition | Example Sentence | Context |
|---|---|---|---|
| Set (Transitive) | To place something in a specific location | Sarah will set the books on the shelf | Requires a direct object |
| Sit (Intransitive) | To rest in a seated position | Michael will sit in the waiting room | Does not require a direct object |
| Set (Figurative) | To establish or fix | The meeting is set for tomorrow | Broader contextual usage |
| Sit (Figurative) | To remain in a particular state | The proposal will sit until next week | Metaphorical application |
| Set (Temporary Placement) | To put something down | Please set the coffee mug here | Physical positioning |
| Sit (Posture) | To assume a seated position | The children sit quietly in class | Personal action |
| Set (Preparation) | To prepare or arrange | We need to set the table for dinner | Organizational action |
| Sit (Remain) | To be located | The package will sit on the porch | Stationary state |
| Set (Solidify) | To become firm or fixed | The concrete will set in an hour | Physical transformation |
| Sit (Legislative) | To be in session | Parliament will sit this afternoon | Formal gathering |
You Might Like: Wife’s or Wives’? Unraveling the Mystery of Possessive Forms
Practical Communication Insights
Language precision demands understanding the subtle differences between these verbs. In professional and personal communication, selecting the correct verb can significantly enhance communication skills and linguistic accuracy.
Contextual Usage Explored
When writing an email or professional correspondence, context becomes paramount. Consider these scenarios:
Email Scenario 1:
To: Emma Thompson
Subject: Conference Preparation
“I will set the presentation materials on the conference table before the meeting begins.”
Email Scenario 2:
To: David Rodriguez
Subject: Office Arrangement
“Please sit in the designated area during the orientation session.”
Grammatical Mechanics
Sentence structure involving set and sit requires careful consideration of tenses. The present, past, and future forms differ significantly:
| Tense | Set Form | Sit Form | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Present Simple | Set | Sit | I set/I sit |
| Present Continuous | Setting | Sitting | I am setting/I am sitting |
| Past Simple | Set | Sat | I set/I sat |
| Past Continuous | Setting | Sitting | I was setting/I was sitting |
| Present Perfect | Set | Sat | I have set/I have sat |
| Future Simple | Will set | Will sit | I will set/I will sit |
You Might Like: Oversight Vs. Oversite: Understanding The Key Differences
Common Mistakes in Usage
Common mistakes often arise from misunderstanding the transitive nature of set. Unlike sit, set typically requires an object. This subtle distinction can create significant grammar clarity challenges.
Writing Tips for Precision
Professional writers and language learners should focus on language learning strategies that emphasize practical examples. Understanding the fundamental differences between set and sit requires consistent practice and contextual awareness.
| Common Error | Correct Usage | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| I will set down | I will sit down | Incorrect object usage |
| The book is setting | The book is sitting | Incorrect verb selection |
| She set on the chair | She sat on the chair | Transitive vs. Intransitive |
| We will set here | We will sit here | Object requirement |
| The meeting set | The meeting sits | Contextual appropriateness |
| I set quietly | I sit quietly | Action specificity |
| The cat set | The cat sits | Animal positioning |
| Setting in the room | Sitting in the room | Verb functionality |
| Set the position | Sit in the position | Precise action |
| Set at the table | Sit at the table | Positional nuance |
You Might Like: “Skill-Set,” “Skillset,” or “Skill Set” | Which is Right?
Phrasal Verb Exploration
Phrasal verbs involving set and sit add another layer of complexity to English grammar. Understanding these variations enhances overall language comprehension and communication effectiveness.

Professional and Academic Significance
Mastering the distinction between set and sit extends beyond casual conversation. Academic writing, professional communication, and precise language usage demand a nuanced understanding of these fundamental verbs.
Advanced Usage Perspectives
Nuanced Linguistic Applications
Language precision becomes increasingly complex when examining the deeper linguistic subtleties of set and sit. Professional communicators must develop a sophisticated understanding that transcends basic grammatical rules.
| Linguistic Context | Set Usage | Sit Usage | Contextual Explanation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Scientific Writing | Set parameters | Sit for observation | Technical precision |
| Legal Documentation | Set conditions | Sit for hearings | Formal communication |
| Literary Expression | Set the scene | Sit in contemplation | Narrative technique |
| Medical Terminology | Set a fracture | Sit for examination | Professional context |
| Architectural Design | Set the foundation | Sit within spaces | Structural planning |
| Psychological Study | Set experimental conditions | Sit in therapeutic sessions | Research methodology |
| Culinary Arts | Set the presentation | Sit for dining | Artistic expression |
| Musical Performance | Set the stage | Sit for rehearsal | Creative preparation |
| Technological Context | Set configurations | Sit idle | System management |
| Diplomatic Interactions | Set negotiations | Sit in conference | International relations |
Semantic Depth of Verbs
Verb usage extends far beyond simple action description. The verbs set and sit carry profound semantic implications that reflect nuanced human experiences and interactions.
Professional Email Example:
To: Alexandra Chen
Subject: Project Management
“We will set the project parameters and sit down to discuss implementation strategies.”
Grammatical Transformations
Understanding tenses and sentence structure requires deep linguistic insight. The metamorphosis of set and sit across different grammatical contexts reveals their remarkable flexibility.
| Grammatical Dimension | Set Characteristics | Sit Characteristics | Interpretative Insights |
|---|---|---|---|
| Active Voice | Actively places | Actively positions | Direct agency |
| Passive Voice | Being positioned | Being seated | Indirect experience |
| Imperative Mood | Set immediately | Sit now | Commanding action |
| Subjunctive Use | Would set | Would sit | Hypothetical scenarios |
| Reflexive Application | Set oneself | Sit oneself | Personal engagement |
| Causative Expressions | Cause to set | Cause to sit | Indirect influence |
| Idiomatic Expressions | Set in motion | Sit tight | Cultural nuances |
| Metaphorical Usage | Set expectations | Sit with uncertainty | Emotional landscape |
| Professional Terminology | Set protocols | Sit in evaluation | Organizational dynamics |
| Academic Discourse | Set theoretical frameworks | Sit in research | Intellectual exploration |
Communication Strategies
Writing tips for mastering these verbs involve understanding their contextual usage. Professional communicators must develop an intuitive sense of linguistic appropriateness.
Practical Learning Approaches
Language learning demands consistent exposure and deliberate practice. Developing communication skills requires moving beyond memorization to understanding deeper linguistic principles.
Comprehensive Linguistic Analysis
English grammar presents intricate challenges that demand sustained attention. The verbs set and sit exemplify the complexity of linguistic expression, requiring nuanced understanding and continuous refinement.
Academic Presentation Scenario:
Presenter: Dr. Michael Ramirez
Conference: Linguistic Innovations
“We set the research parameters and sit prepared to explore groundbreaking discoveries.”
Cultural and Linguistic Variations
Different English-speaking regions demonstrate subtle variations in set and sit usage. These linguistic accuracy differences reflect broader cultural communication patterns.
| Regional Variation | Set Interpretation | Sit Interpretation | Cultural Nuance |
|---|---|---|---|
| British English | More formal placement | More precise positioning | Traditional usage |
| American English | Broader application | More casual interpretation | Dynamic approach |
| Australian English | Practical orientation | Relaxed positioning | Contextual flexibility |
| Canadian English | Precise implementation | Comfortable seating | Balanced approach |
| Indian English | Structured placement | Formal seating | Hierarchical implications |
| Caribbean English | Creative positioning | Relaxed interpretation | Cultural fusion |
| South African English | Systematic arrangement | Deliberate positioning | Multicultural influence |
| New Zealand English | Practical application | Comfortable arrangement | Adaptive usage |
| Scottish English | Precise setting | Specific seating | Linguistic distinctiveness |
| Irish English | Narrative placement | Conversational positioning | Storytelling approach |
Final Reflections
Mastering the verbs set and sit represents a journey of language learning that extends beyond grammatical rules. It involves understanding the subtle dance of linguistic expression, where each word carries a universe of meaning.
Professional communicators, writers, and language enthusiasts must approach these verbs with curiosity, respect, and an ongoing commitment to grammatical clarity. The art of choosing between set and sit is not merely about following rules but about capturing the essence of human experience through precise language.

Emma Carter is an experienced blogger at Vocablarified. She enjoys helping people expand their vocabulary and improve their language skills. With a warm and approachable writing style, Emma makes learning new words fun and accessible. When she’s not writing, she loves reading books and discovering new phrases to share with her readers. Emma is passionate about making language learning an enjoyable journey for everyone.